This document provides a comprehensive overview of the Hotelaro system's database schema, including table structures, relationships, and the multi-tenant data isolation patterns. It covers the database design that supports the hotel booking system, restaurant operations, user management, and system configuration.
For information about how this database schema integrates with the overall system architecture, see System Architecture. For details on authentication and user management that utilizes these tables, see Authentication & Security.
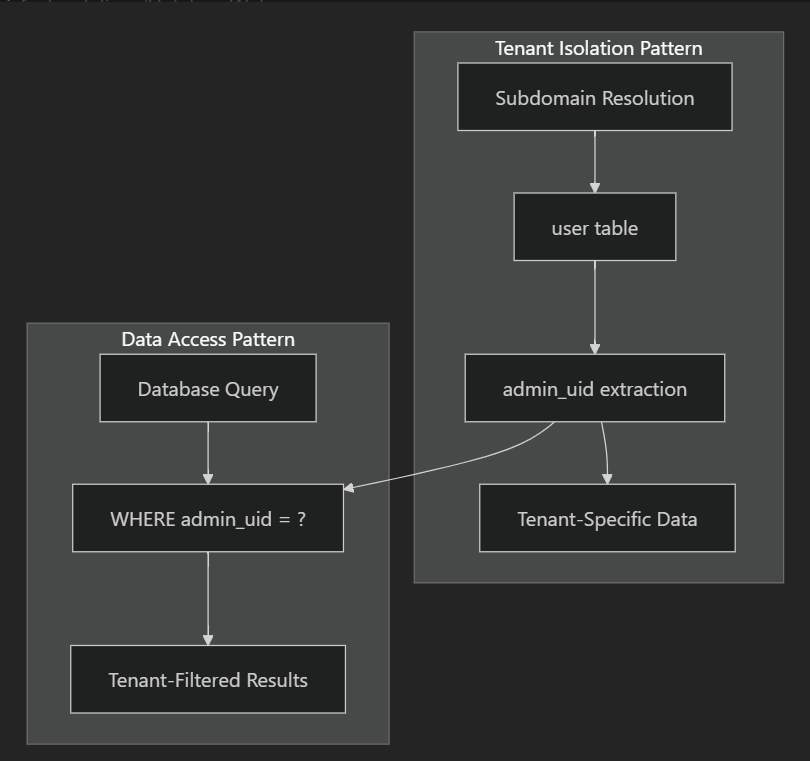
The Hotelaro system implements a shared database multi-tenant architecture where all hotel properties share the same database tables, but data is isolated using an admin_uid field as the tenant identifier.
| Table | Purpose | Key Fields |
|---|---|---|
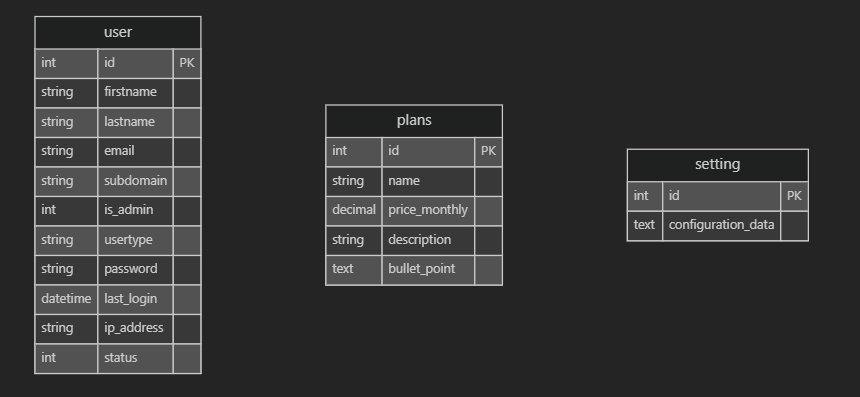
| user | Main user accounts and hotel properties | id, email, subdomain, firstname, lastname, is_admin, usertype |
| setting | Global system settings | Configuration parameters |
| plans | Subscription plans for hotel properties | id, name, price_monthly, description |
The hotel booking system uses tables prefixed with hotel_booking_ to manage reservations, rooms, and related data.
| Table | Purpose | Multi-Tenant |
|---|---|---|
| hotel_booking_bookings | Guest reservations and booking details | Yes (admin_uid) |
| hotel_booking_rooms | Individual room configurations | Yes (admin_uid) |
| hotel_booking_room_type | Room type definitions | Yes (admin_uid) |
| hotel_booking_floors | Hotel floor management | Yes (admin_uid) |
| hotel_booking_setup | Hotel-specific configuration | Yes (admin_uid) |
| Table | Purpose |
|---|---|
| hotel_booking_amenitis | Hotel amenities and features |
| hotel_booking_webbuilder_sections | Website customization data |
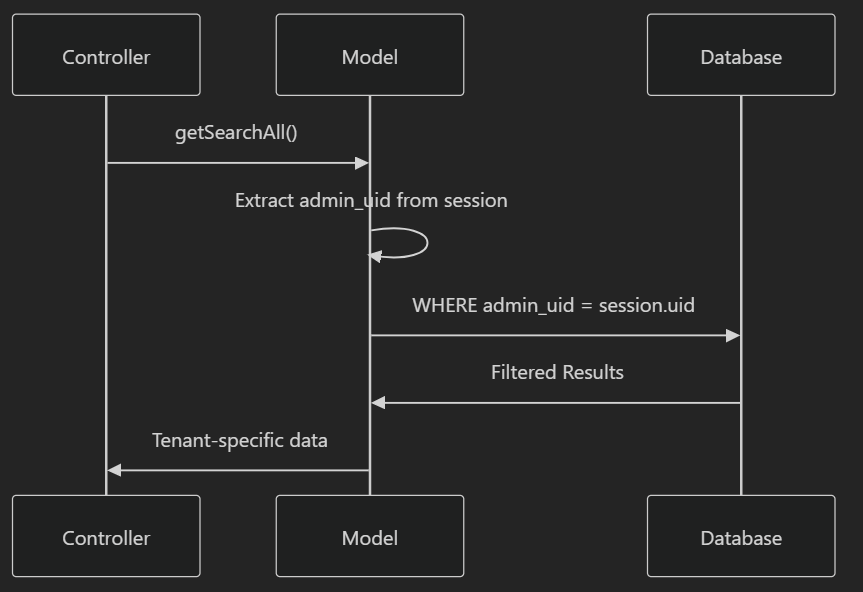
All queries in the system follow a consistent pattern for tenant isolation:
SELECT * FROM hotel_booking_[table] WHERE admin_uid = ?
This pattern is implemented across all model classes:

The system follows consistent naming patterns:
| Prefix | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| hotel_booking_ | Core booking functionality | hotel_booking_rooms |
| hotel_booking_item_ | Restaurant/menu items | hotel_booking_item_foods |
| No prefix | System-wide tables | user, setting, plans |
All hotel-specific tables include an admin_uid field for tenant isolation, while system-wide tables do not require this field.
The system maintains referential integrity through: