This document describes the multi-tenant architecture of the Hotelaro hotel management system. The multi-tenant system enables multiple hotel properties to operate independently on a single platform instance using subdomain-based tenant isolation and admin_uid filtering.
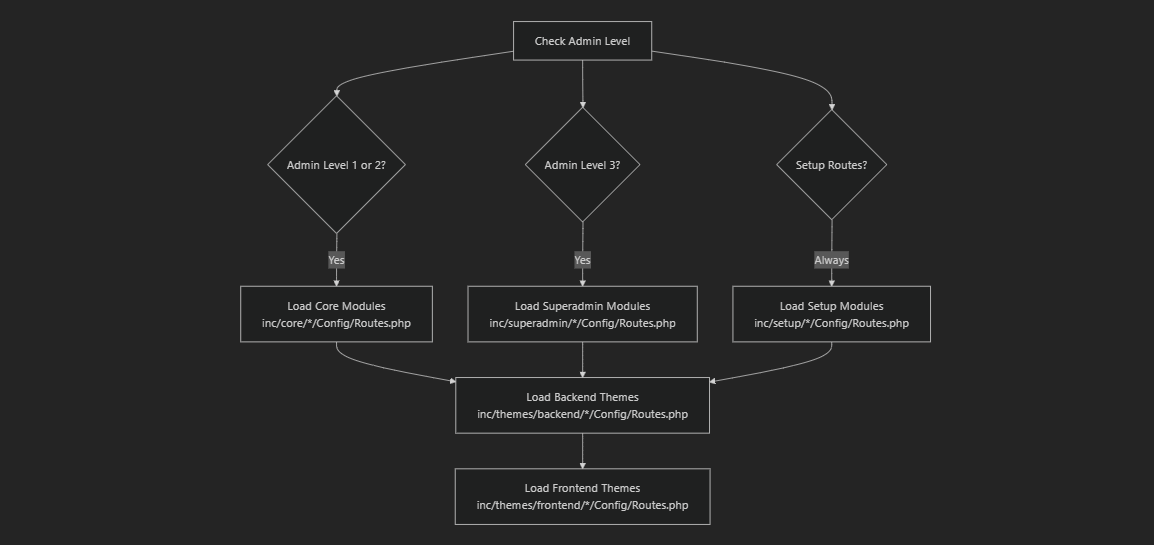
The system supports different access levels and dynamically loads appropriate modules based on user permissions. For information about authentication and user roles, see Authentication & Security. For database structure details, see Database Schema.
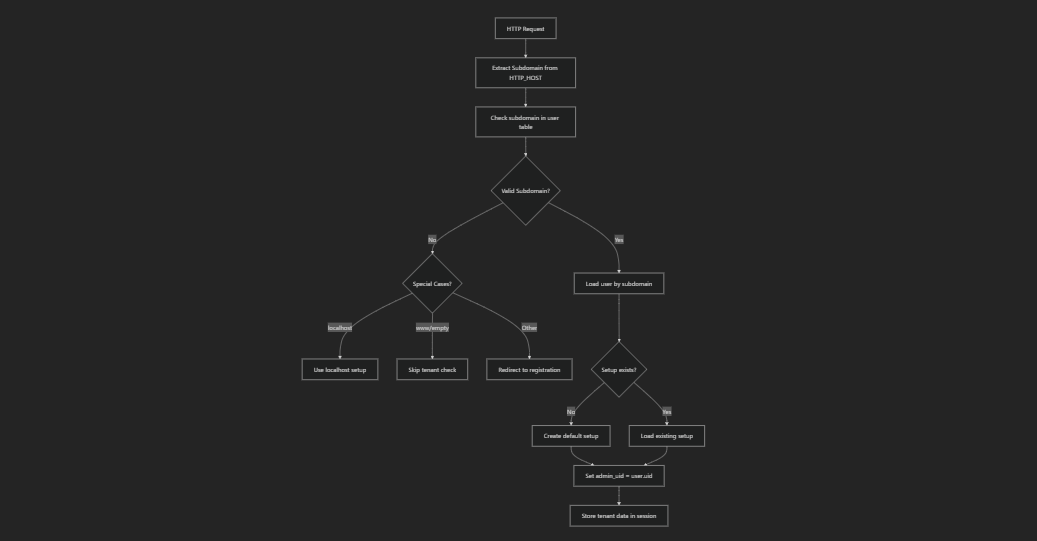
The multi-tenant system identifies tenants through subdomain extraction from the HTTP host header. Each subdomain corresponds to a unique hotel property with its own isolated data and configuration.
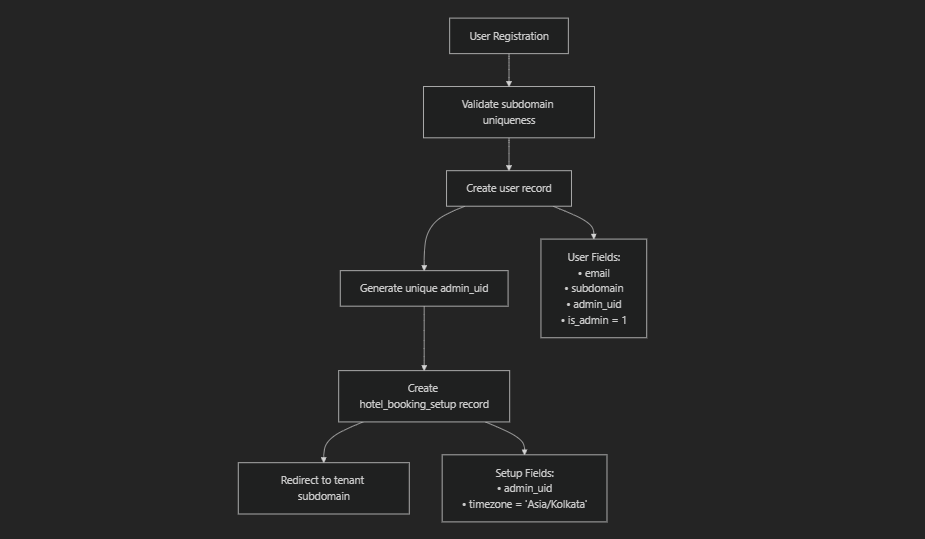
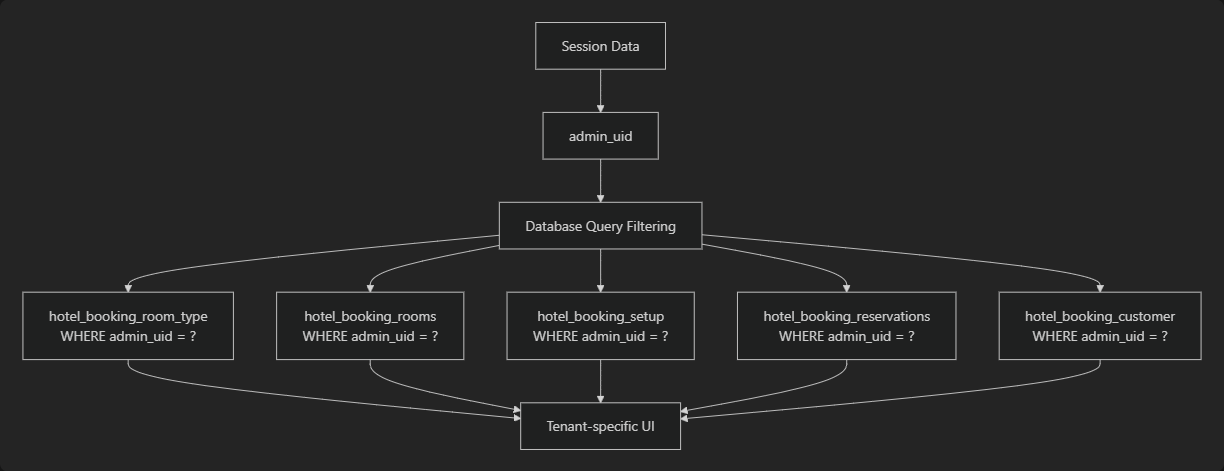
The multi-tenant system ensures data isolation through the admin_uid field, which is consistently applied across all tenant-specific database operations and UI components.
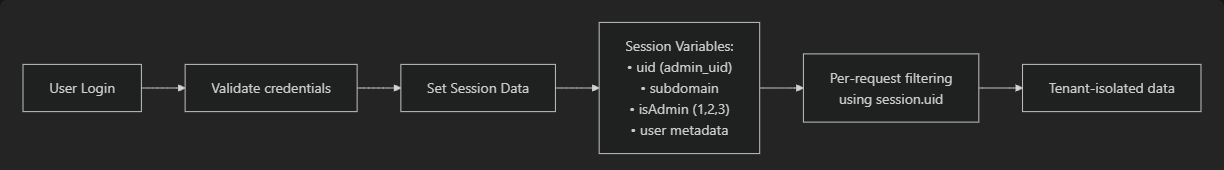
The system dynamically loads different sets of routes based on user admin levels, providing role-based access to system modules.
The AuthCheck filter validates tenant access on every request to ensure only valid subdomains can access the system.
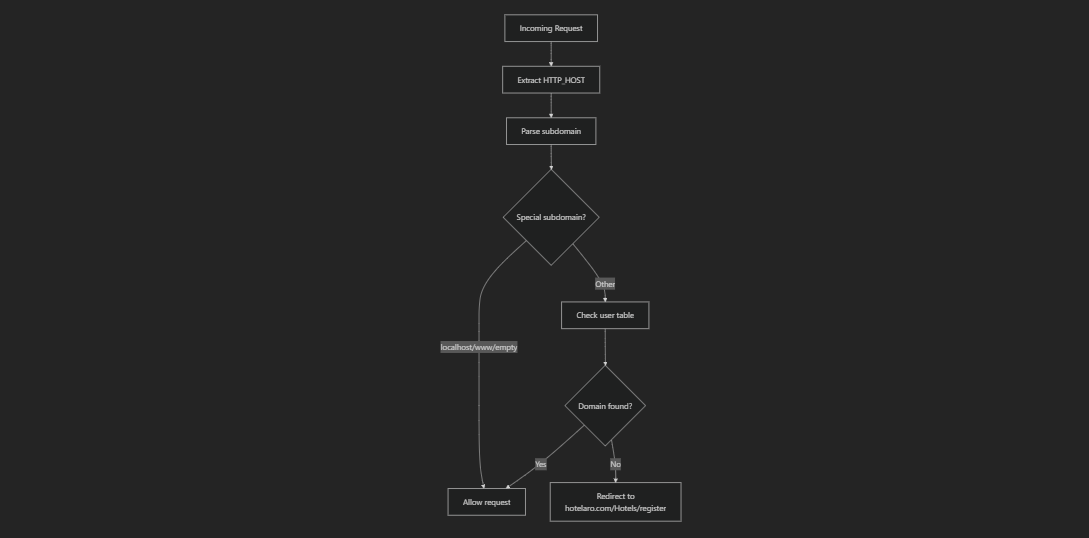
The authentication filter is configured as a global filter that runs on all requests:
The multi-tenant system integrates with the database schema through consistent admin_uid foreign key relationships across all tenant-specific tables.
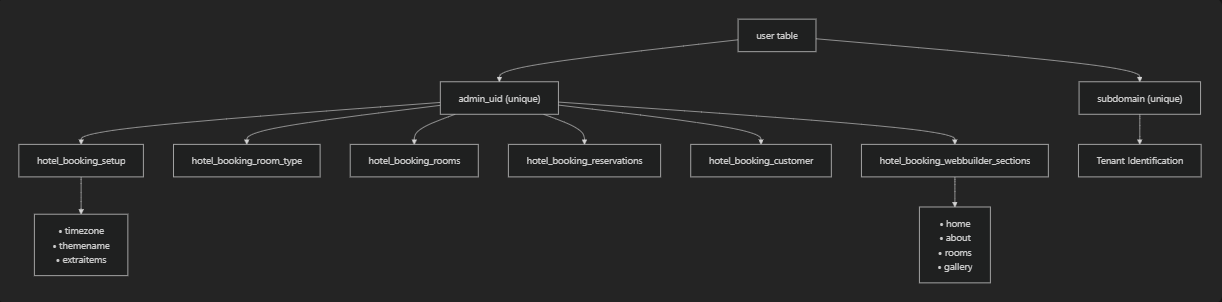
All tenant-specific operations follow consistent patterns for data isolation:
This ensures complete data isolation between tenants while maintaining a single database instance for operational efficiency.